INDUSTRY NEWS
Difficulties in the control of brushless motors without indu
Brushless and sensorless control is extremely widespread in practice and has been studied for a long time in particular.
Its control difficulties are mainly twofold.
Firstly, the starting of the motor.
Secondly, the detection of the rotor position.
For the high-voltage induction programme, in addition to the software difficulties, the hardware design should not be ignored, such as the hardware design is slightly improper, will lead to the entire control board interference is very large, thus increasing the difficulty of the entire programme success.
The following we mainly focus on low-voltage non-inductance program to discuss, for low-voltage non-inductance program, the hardware design on the market are more or less the same, the way to detect the position of the rotor are also almost all use counter-electromotive force detection method.
1. Why is it so difficult to start a motor without inductors?
For brushless motors, the operation of the motor is controlled by the electronic switch phase change, then you want the motor to run normally and efficiently, you must know the position of the rotor after the normal phase change, the problem comes, the motor does not have a sensor, and did not turn up, so the location of the rotor is unknown, so the start of the sensorless should be self-starting, let the motor rotate at a certain rate first, in the process of the motor automatically, we know the position of the rotor by detecting the counter-electromotive force, so as to get the correct phase change.
Self-starting of motors is easier said than done, and we have summarised the following experiences for reference during the commissioning of numerous induction-free programmes.
(1), first of all, the self-start, self-start must make the motor run smoothly, not to shake, and at the same time not to cause high current. This is a very critical step in the success of the start. Specific how to achieve this effect, we have to adjust the PWM duty cycle and the length of the phase change time in the process of commissioning.
(2), the number of starting steps can not be too few, not too much, generally ten or so steps is enough, and so the motor running ten or so steps to start detecting the counter-electromotive force, when the detection of the correct counter-electromotive force at this time the motor will run normally up.
2, how to detect the counter-electromotive force detection of counter-electromotive force there are two methods, the first is to use the microcontroller internal AD sampling counter-electromotive force signal to compare, the second is to use the comparator to directly compare. These two methods are the same idea, but according to personal experience, with the comparator program more reliable, better performance, especially when the motor speed requirements are very high, with AD sampling method is almost unfeasible. Although the comparator solution is more advantageous, why is it so common to use AD sampling in the market?
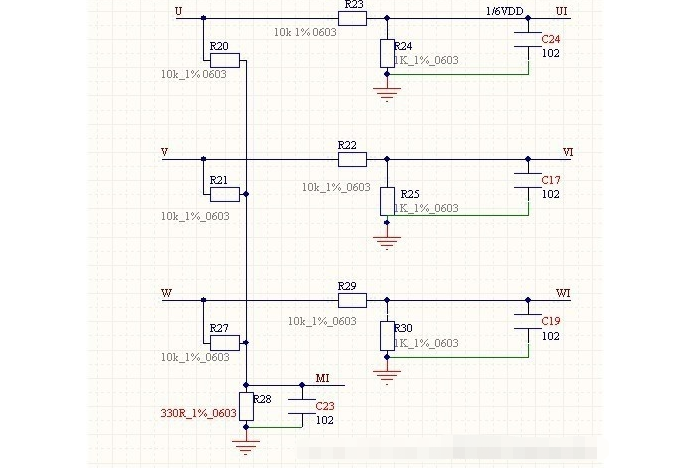
This is mainly due to the cost of the product. To do with the comparator scheme, either add a comparator IC externally, not only to increase the cost, but also to increase the PCB layout space, the second is to find an internal microcontroller with AD, and this microcontroller is usually relatively speaking, the price is a bit higher. The following diagram is a circuit reference diagram for detecting the counter-electromotive force: this is an AD detection scheme, comparator comparison scheme common circuit diagram, if the microcontroller has a comparator, it will be connected to the comparator of that port, if not, it must be connected to the AD port.
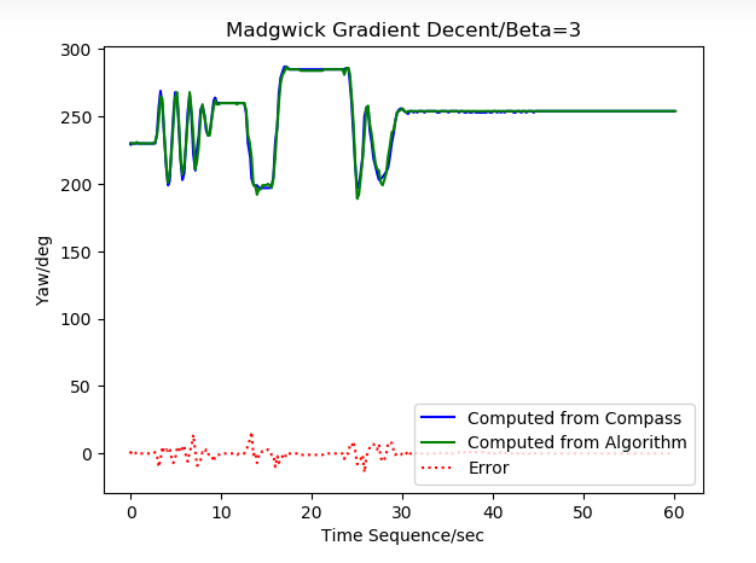
Take the comparator scheme as an example, when the motor rotation is completed, open the comparator interrupt (compare the object: the voltage of the midpoint and the voltage value of the suspended phase), when the comparator interrupt comes, immediately change the phase, change the phase and then set the comparator comparison pair, that is, the voltage of the midpoint and the voltage value of the current suspended phase, in order to wait for the arrival of the next comparison interrupt.
The above control method is a control method without a delay of 30 degrees, in the general control system, this control method is feasible, especially to do the inductorless high current and high torque scheme, the control method without delay will be more stable instead, and the load carrying capacity will be stronger. Of course there is a downside to this, in that it is not as efficient as adding a 30 degree delay. The exact way to do this will depend on the actual product.