INDUSTRY NEWS
What are the classifications of motors? What are its main ap
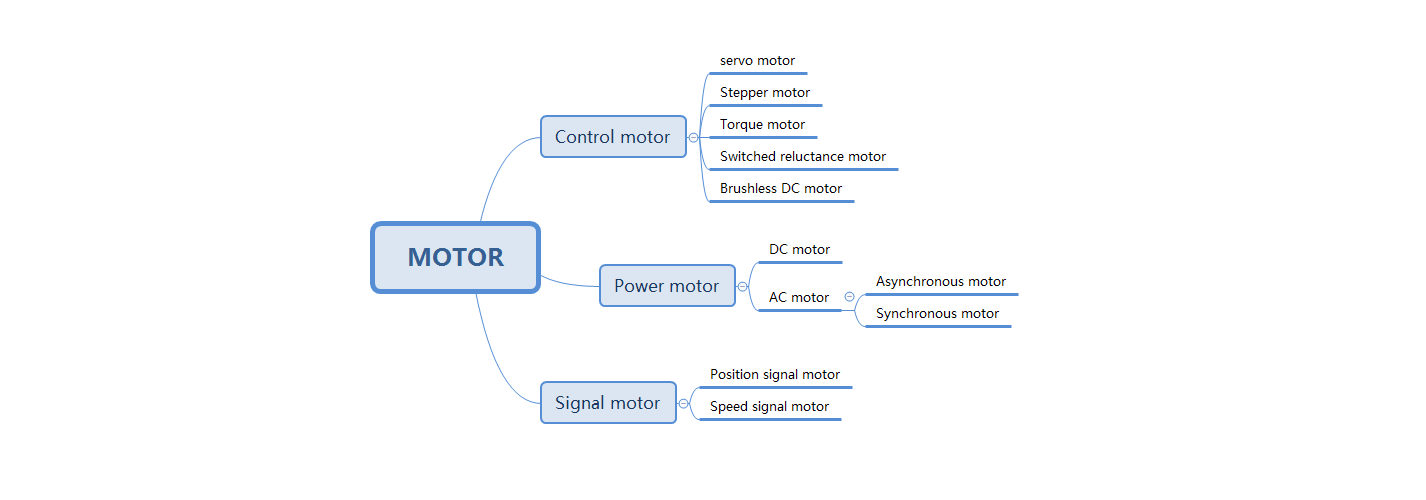
As we all know, the motor is an important part of the transmission and control system. With the development of modern science and technology, the focus of the motor in practical applications has begun to shift from the simple transmission in the past to the complex control; especially the speed and position of the motor. , Accurate control of torque. However, motors have different designs and driving methods according to different applications. At first glance, it seems that the selection is very complicated. Therefore, people have carried out basic classifications according to the purpose of rotating motors. Below we will introduce step by step the most representative, most commonly used, and most basic motors in motors-control motors, power motors, and signal motors.
Control motor
The control motor is mainly used for precise speed and position control, and is used as an "executor" in the control system. It can be divided into servo motors, stepping motors, torque motors, switched reluctance motors, and DC brushless motors.
1. Servo motor
Servo motors are widely used in various control systems. They can convert the input voltage signal into a mechanical output on the motor shaft and drag the controlled components to achieve the purpose of control. Generally, the servo motor requires that the speed of the motor be controlled by the applied voltage signal; the speed can change continuously with the change of the applied voltage signal; the torque can be controlled by the current output by the controller; the response of the motor should be fast, The volume should be small, and the control power should be small. Servo motors are mainly used in various motion control systems, especially servo systems.
Servo motors are divided into DC and AC. The earliest servo motors are ordinary DC motors. When the control accuracy is not high, ordinary DC motors are used as servo motors. With the rapid development of permanent magnet synchronous motor technology, most of the servo motors refer to AC permanent magnet synchronous servo motors or DC brushless motors.
2. Stepping motor
The so-called stepper motor is an actuator that converts electrical pulses into angular displacement; more generally speaking: when the stepper driver receives a pulse signal, it drives the stepper motor to rotate a fixed angle in the set direction. We can control the angular displacement of the motor by controlling the number of pulses, so as to achieve the purpose of precise positioning; at the same time, we can also control the speed and acceleration of the motor rotation by controlling the pulse frequency, so as to achieve the purpose of speed regulation. At present, the more commonly used stepping motors include reactive stepping motors (VR), permanent magnet stepping motors (PM), hybrid stepping motors (HB) and single-phase stepping motors.
The main difference between stepper motor and ordinary motor lies in its pulse drive form. It is precisely this characteristic that stepper motor can be combined with modern digital control technology. But stepper motors are not as good as traditional closed-loop control DC servo motors in terms of control accuracy, speed range, and low-speed performance; so they are mainly used in occasions where accuracy requirements are not particularly high. Because the stepper motor has the characteristics of simple structure, high reliability and low cost, the stepper motor is widely used in various fields of production practice; especially in the field of CNC machine tool manufacturing, since the stepper motor does not require A/D conversion, it can The digital pulse signal is directly converted into angular displacement, so it has always been regarded as the most ideal CNC machine tool actuator.
In addition to the application in CNC machine tools, stepper motors can also be used in other machinery, such as as the motor in automatic feeders, as the motor of general floppy disk drives, and can also be used in printers and plotters.
In addition, the stepper motor also has many defects; because the stepper motor has a no-load starting frequency, the stepper motor can run normally at low speed, but if it is higher than a certain speed, it cannot start, accompanied by a sharp whistling sound; different The precision of the subdivision drivers of manufacturers may vary greatly. The greater the subdivision number, the more difficult it is to control; and the stepper motor has greater vibration and noise when it rotates at a low speed.
3. Torque motor
The so-called torque motor is a flat multi-pole permanent magnet DC motor. The armature has more slots, commutation pieces and series conductors to reduce torque pulsation and speed pulsation. There are two types of torque motors: DC torque motors and AC torque motors.
Among them, the self-inductance of the DC torque motor is very small, so the response is very good; its output torque is proportional to the input current, and has nothing to do with the speed and position of the rotor; it can be directly connected to the load and run at low speed in the state of close to the locked rotor. There is no gear reduction, so a high torque to inertia ratio can be produced on the loaded shaft, and system errors due to the use of reduction gears can be eliminated.
AC torque motors can be divided into two types: synchronous and asynchronous. At present, the squirrel-cage asynchronous torque motor is commonly used, which has the characteristics of low speed and high torque. Generally, AC torque motors are often used in the textile industry. Their working principle and structure are the same as single-phase asynchronous motors. However, due to the larger resistance of the squirrel-cage rotor, its mechanical characteristics are softer.
4. Switched reluctance motor
Switched reluctance motor is a new type of speed-regulating motor with extremely simple and sturdy structure, low cost, and excellent speed-regulating performance. It is a strong competitor of traditional control motors and has a strong market potential. However, there are also problems such as torque ripple, running noise and vibration, and it takes some time to optimize and improve to adapt to actual market applications.
5. Brushless DC Motor
Brushless DC motor (BLDCM) is developed on the basis of brushed DC motor, but its driving current is uncompromising AC; brushless DC motor can be divided into brushless speed motor and brushless torque motor . Generally, there are two drive currents for brushless motors, one is a trapezoidal wave (usually a "square wave"), and the other is a sine wave. Sometimes the former is called a DC brushless motor, and the latter is called an AC servo motor. To be precise, it is also a kind of AC servo motor.
In order to reduce the moment of inertia, the brushless DC motor usually adopts a "slender" structure. Brushless DC motors are much smaller in weight and volume than brushed DC motors, and the corresponding moment of inertia can be reduced by about 40%-50%. Due to the processing problems of permanent magnet materials, the general capacity of brushless DC motors is below 100kW.
This kind of motor has good linearity of mechanical characteristics and adjustment characteristics, wide speed range, long life, easy maintenance, low noise, and there is no series of problems caused by brushes, so this kind of motor is very important in the control system. Application potential.


Control motor
The control motor is mainly used for precise speed and position control, and is used as an "executor" in the control system. It can be divided into servo motors, stepping motors, torque motors, switched reluctance motors, and DC brushless motors.
1. Servo motor
Servo motors are widely used in various control systems. They can convert the input voltage signal into a mechanical output on the motor shaft and drag the controlled components to achieve the purpose of control. Generally, the servo motor requires that the speed of the motor be controlled by the applied voltage signal; the speed can change continuously with the change of the applied voltage signal; the torque can be controlled by the current output by the controller; the response of the motor should be fast, The volume should be small, and the control power should be small. Servo motors are mainly used in various motion control systems, especially servo systems.
Servo motors are divided into DC and AC. The earliest servo motors are ordinary DC motors. When the control accuracy is not high, ordinary DC motors are used as servo motors. With the rapid development of permanent magnet synchronous motor technology, most of the servo motors refer to AC permanent magnet synchronous servo motors or DC brushless motors.
2. Stepping motor
The so-called stepper motor is an actuator that converts electrical pulses into angular displacement; more generally speaking: when the stepper driver receives a pulse signal, it drives the stepper motor to rotate a fixed angle in the set direction. We can control the angular displacement of the motor by controlling the number of pulses, so as to achieve the purpose of precise positioning; at the same time, we can also control the speed and acceleration of the motor rotation by controlling the pulse frequency, so as to achieve the purpose of speed regulation. At present, the more commonly used stepping motors include reactive stepping motors (VR), permanent magnet stepping motors (PM), hybrid stepping motors (HB) and single-phase stepping motors.
The main difference between stepper motor and ordinary motor lies in its pulse drive form. It is precisely this characteristic that stepper motor can be combined with modern digital control technology. But stepper motors are not as good as traditional closed-loop control DC servo motors in terms of control accuracy, speed range, and low-speed performance; so they are mainly used in occasions where accuracy requirements are not particularly high. Because the stepper motor has the characteristics of simple structure, high reliability and low cost, the stepper motor is widely used in various fields of production practice; especially in the field of CNC machine tool manufacturing, since the stepper motor does not require A/D conversion, it can The digital pulse signal is directly converted into angular displacement, so it has always been regarded as the most ideal CNC machine tool actuator.
In addition to the application in CNC machine tools, stepper motors can also be used in other machinery, such as as the motor in automatic feeders, as the motor of general floppy disk drives, and can also be used in printers and plotters.
In addition, the stepper motor also has many defects; because the stepper motor has a no-load starting frequency, the stepper motor can run normally at low speed, but if it is higher than a certain speed, it cannot start, accompanied by a sharp whistling sound; different The precision of the subdivision drivers of manufacturers may vary greatly. The greater the subdivision number, the more difficult it is to control; and the stepper motor has greater vibration and noise when it rotates at a low speed.
3. Torque motor
The so-called torque motor is a flat multi-pole permanent magnet DC motor. The armature has more slots, commutation pieces and series conductors to reduce torque pulsation and speed pulsation. There are two types of torque motors: DC torque motors and AC torque motors.
Among them, the self-inductance of the DC torque motor is very small, so the response is very good; its output torque is proportional to the input current, and has nothing to do with the speed and position of the rotor; it can be directly connected to the load and run at low speed in the state of close to the locked rotor. There is no gear reduction, so a high torque to inertia ratio can be produced on the loaded shaft, and system errors due to the use of reduction gears can be eliminated.
AC torque motors can be divided into two types: synchronous and asynchronous. At present, the squirrel-cage asynchronous torque motor is commonly used, which has the characteristics of low speed and high torque. Generally, AC torque motors are often used in the textile industry. Their working principle and structure are the same as single-phase asynchronous motors. However, due to the larger resistance of the squirrel-cage rotor, its mechanical characteristics are softer.
4. Switched reluctance motor
Switched reluctance motor is a new type of speed-regulating motor with extremely simple and sturdy structure, low cost, and excellent speed-regulating performance. It is a strong competitor of traditional control motors and has a strong market potential. However, there are also problems such as torque ripple, running noise and vibration, and it takes some time to optimize and improve to adapt to actual market applications.
5. Brushless DC Motor
Brushless DC motor (BLDCM) is developed on the basis of brushed DC motor, but its driving current is uncompromising AC; brushless DC motor can be divided into brushless speed motor and brushless torque motor . Generally, there are two drive currents for brushless motors, one is a trapezoidal wave (usually a "square wave"), and the other is a sine wave. Sometimes the former is called a DC brushless motor, and the latter is called an AC servo motor. To be precise, it is also a kind of AC servo motor.
In order to reduce the moment of inertia, the brushless DC motor usually adopts a "slender" structure. Brushless DC motors are much smaller in weight and volume than brushed DC motors, and the corresponding moment of inertia can be reduced by about 40%-50%. Due to the processing problems of permanent magnet materials, the general capacity of brushless DC motors is below 100kW.
This kind of motor has good linearity of mechanical characteristics and adjustment characteristics, wide speed range, long life, easy maintenance, low noise, and there is no series of problems caused by brushes, so this kind of motor is very important in the control system. Application potential.